Light & shadows
Material surfaces cast shadows when they obstruct light sources.
Light
Light and shadows
In the Material Design environment, virtual lights illuminate the UI. Key lights create sharper, directional shadows, called key shadows. Ambient light appears from all angles to create diffused, soft shadows, called ambient shadows.

Shadow cast by a key light.

Shadow cast by ambient light.

Combined shadow from key and ambient lights.
Elements use shadows on dark surfaces, even if they are less visible.
Light sources
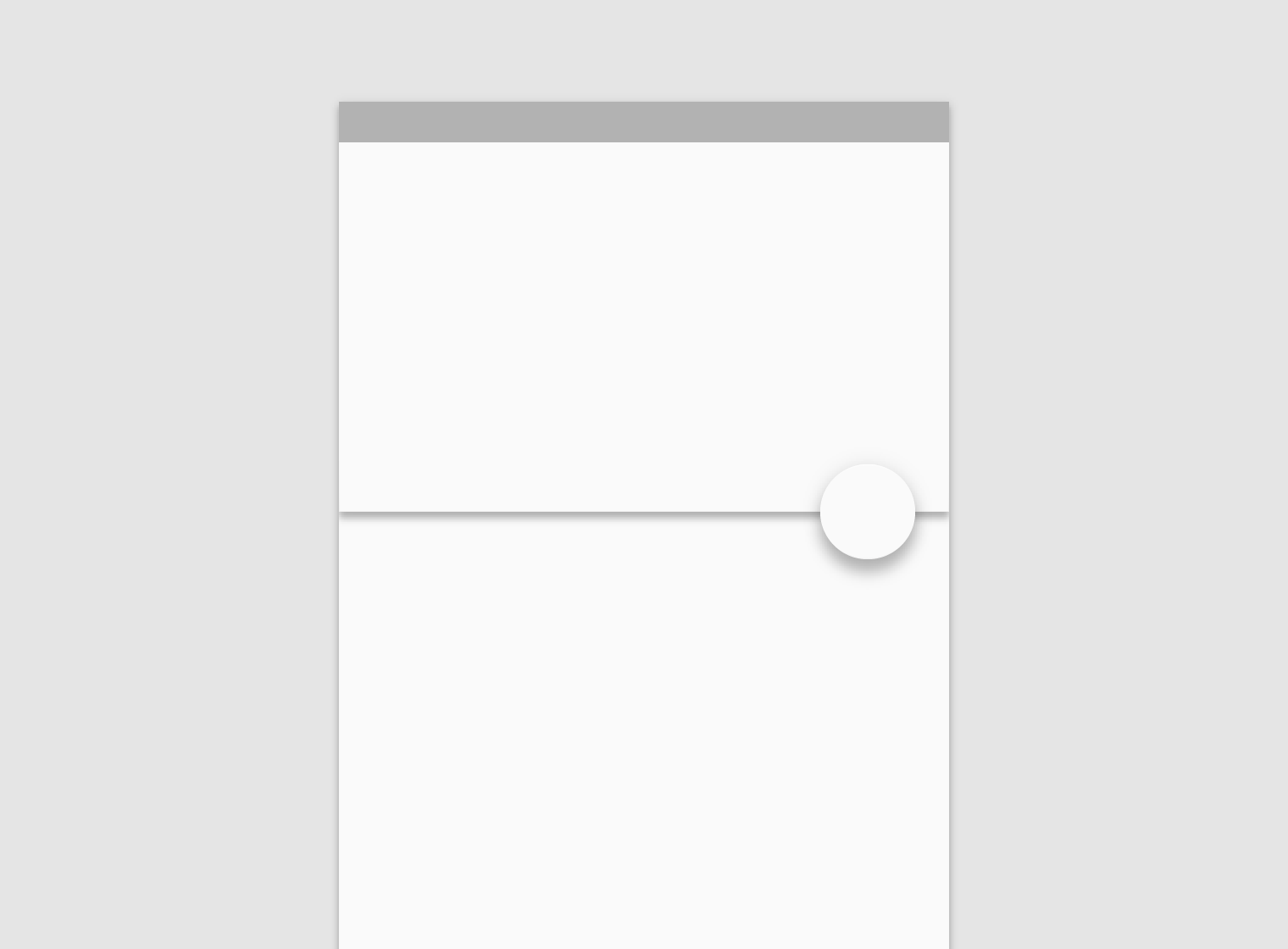
Shadows in the Material environment are cast by a key light and ambient light. In Android and iOS development, shadows occur when light sources are blocked by Material surfaces at various positions along the z-axis. On the web, shadows are depicted by manipulating the y-axis only. The following example shows a card with an elevation of 6dp.
Shadows
Shadows provide cues about depth, direction of movement, and surface edges. A surface’s shadow is determined by its elevation and relationship to other surfaces.
Usage
Because shadows express the degree of elevation between surfaces, they must be used consistently throughout your product.
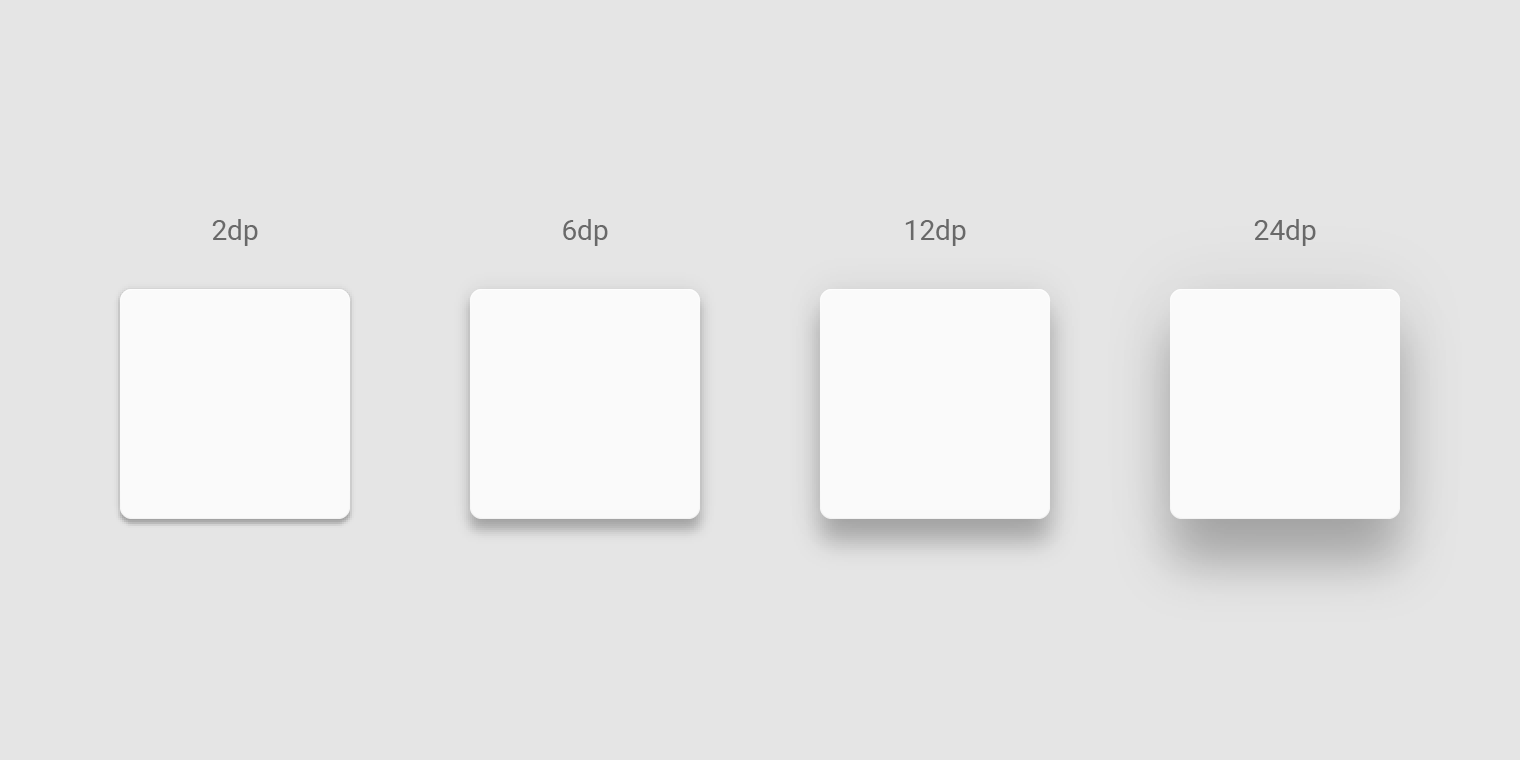
Elevation is depicted by consistent use of shadow.
Shadow size reflects elevation. Surfaces at higher elevations have larger shadows, while those at lower elevations have smaller shadows.
Shadows & Motion
Shadows provide useful cues about a surface’s direction of movement and whether the distance between surfaces is increasing or decreasing.